The United Arab Emirates: a chronology
- Alessio Pimpinelli
- Dec 21, 2022
- 4 min read
Updated: May 5, 2023
From sandy backwater to glitzy global Dubai and oil-rich Abu Dhabi, the United Arab Emirates' fast rise to power and prominence on the global stage has been something truly extraordinary. As the country has just celebrated its fiftieth anniversary, it is noteworthy to retrace the steps which have brought the emirates to be where they stand today.
1793: Abu Dhabi is founded by members of the Bani Yas tribe from the Liwa Oasis region.
1819: Ras Al-Khaimah, the most prominent settlement at the time, is looted and razed to the ground by the British in an attempt to counter maritime piracy in the Gulf.
1820: The British impose on the local tribes a General Treaty of Maritime Peace; a British local Resident settles down in the Gulf to oversee the Treaty's enforcement.
1833: Dubai is founded when a section of the Bani Yas tribe in Abu Dhabi secedes and moves northwards.
1835: The local sheikhs sign with the British a Maritime Truce, which aims to completely eradicate maritime inter-fighting and which extends British protection to the rulers of Abu Dhabi, Dubai, Sharjah, Ras Al-Khaimah and Ajman (which from now on are referred as 'Trucial States').
1892: On the wave of imperialist feelings, Britain concludes an Exclusive Agreement with the rulers of the Trucial States, whose purpose is preventing other European powers (namely Germany) from exerting any influence in the area. Britain thus takes complete control over the foreign affairs of the sheikhdoms.
1930s: Pearling, the most lucrative trade activity in the Gulf, rapidly declines due to the Great Depression and to the introduction of a cheaper type of pearl from Japan.
1955: The "Buraimi Oasis Dispute" is resolved in favour of Abu Dhabi when the Saudis, who had claimed control over the area, are evicted for good.
1958: Oil is discovered in Abu Dhabi in commercial quantities.
1966: Oil is discovered in Dubai in commercial quantities
In Abu Dhabi, Sheikh Zayed becomes the ruler after deposing his brother Shakhbut in a bloodless coup. He will be considered the father of the future nation.
1971: Two days before the British formal withdrawal from the area, Iran seizes the islands of Abu Musa and Greater and Lesser Tunbs which belonged to Sharjah and Ras Al- Khaimah respectively. Iran holds the islands to this day.
Six Trucial States (all but Ras Al-Khaimah) sign the Constitution of the impending UAE.
On December 2, the United Arab Emirates are formed (Ras al-Khaimah will belatedly join in the following February).
A detailed political map of the UAE from vidiani.com
1972: The newly-created UAE joins the International Monetary Fund.
1973: The UAE Dirham is created.
Abu Dhabi participates in the oil embargo spearheaded by King Faisal of Saudi Arabia against the West in response to the events of the Yom Kippur War.
1976: The Abu Dhabi Sovereign Wealth Fund (through the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority) is created. It remains the third largest in the world to this day, and the largest in the Middle East.
1978: The Union Defence Force is created, although military unification among the several emirates will not be completely achieved until the 1990s.
1980: The Central Bank is created.
1981: The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is formed.
1983: Dubai's new Jebel Ali port opens.
1985: Emirates Airways is established in Dubai.
1993: The UAE signs a Bilateral Investment Treaty with China.
1994: The UAE signs a Defence Cooperation Agreement with the USA.
1995: A formal Defence Agreement with France is signed.
2003: Etihad Airways is established in Abu Dhabi.

Emirates and Etihad, the two global airlines which today are synonymous with high comfort and luxury. Image from 24newdhd.tv
2004: Sheikh Zayed of Abu Dhabi dies. His third son Mohamed bin Zayed (MBZ) becomes the power behind the throne of his half-brother Khalifa.
The Dubai International Financial Centre and Stock Exchange are established.
2006: Mohamed bin Rashid (MBR) becomes the ruler of Dubai. His relationship with MBZ is what will propel the UAE forward in the incoming years.
2007: The UAE signs a Defence Cooperation Agreement with Australia.
2008: Financial Crisis; Abu Dhabi bails out Dubai.
The Abu Dhabi Declaration for the protection and improvement of migrant workers' rights is signed.
The UAE joins the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium, which marks a deepening of defence and security cooperation with India.
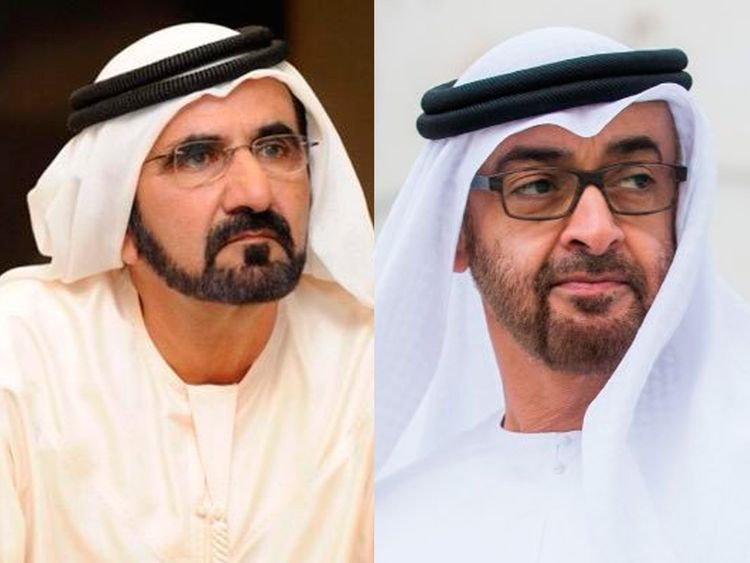

MBR (left) and MBZ (right), rulers of Dubai and Abu Dhabi respectively. Image from Gulfnews.com
2011: Arab Spring; the UAE government heavily cracks down on Islamists at home.
A formal relationship with NATO is established (the first time an Arab state does so).
The government assists the overthrow of Gaddafi and the 'nationalist' cause in Libya.
2013: The UAE supports Al-Sisi's coup in Egypt.
2014: First diplomatic crisis with Qatar, accused of supporting the Islamist Muslim Brotherhood.
The UAE joins the coalition against ISIS and authorises air strikes over Syria and Iraq.
2015: The UAE joins the Saudi Arabia-led coalition in Yemen against the Houtis, Shia rebels believed to be backed by Iran.
2017-2021: Second diplomatic crisis with Qatar, which embargoed and isolated the Qatari peninsula for a while.
2020: The Abraham Accords with Israel are signed; the UAE recognises Israel and establishes formal diplomatic relations with it.
The phased out military withdrawal from Yemen is completed.
2022: MBZ becomes ruler of Abu Dhabi and President of the UAE.
Further Reading:
Coates Ulrichsen, Christian 2017. The United Arab Emirates: Power, Politics and Policymaking. London and New York: Routledge.
Davidson, Christopher (ed.) 2011. Power and politics in the Persian Gulf. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Davidson, Christopher 2021. From Sheikhs to Sultanism: Statecraft and Authority in Saudi Arabia and the UAE. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
.png)




Comments